
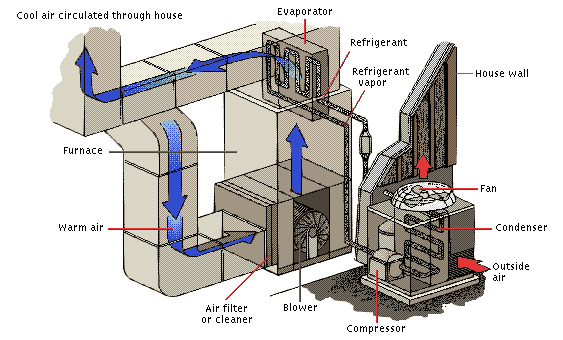
Though your definitions of "comfort" may be different than your neighbor’s, knowing these terms can help make your search for improved comfort and efficiency much more effective. The diagram to the left explains the processes of a central air unit.
Advanced Reciprocating Compressor—Type of compressor that uses a more efficient process for compressing refrigerant for better cooling efficiency.
AFUE—Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency. Indicated as a percentage, your furnace’s AFUE tells how much energy is being converted to heat. For example, an AFUE of 90 means that 90% of the fuel is being used to warm your home, while the other 10% escapes as exhaust with the combustion gases.
BTU—British Thermal Unit. BTU is a measure of the heat expended when fuel is combusted. For cooling, it’s a measure of heat extracted. One BTU is equal to the heat given off by a wooden kitchen match.
Capacity—The ability of a heating or cooling system to heat or cool a given amount of space. For heating, this is usually expressed in BTUs. For cooling, it is given in tons.
Condenser Coil—Part of the outdoor portion of a split-system air conditioner or heat pump. By converting refrigerant that is in a gas form back to a liquid, the coil sends heat carried by the refrigerant to the outside.
Downflow—A type of furnace that takes cool air from the top and blows warm air to the bottom—common where your furnace must be located in a second-floor closet or utility area.
Electronic Air Cleaner (EAC)—An electronic device that filters out large particles and contaminants in indoor air. It then electronically pulls out tiny particles that have been magnetized, such as viruses and bacteria, drawing them to a collector plate.
Load Estimate—A series of studies performed to determine the heating or cooling requirements of your home. An energy load analysis uses information such as the square footage of your home, window or door areas, insulation quality and local climate to determine the heating and cooling capacity needed by your furnace, heat pump or air conditioner. When referring to heating, this is often known as a Heat Loss Analysis, since a home’s heating requirements are determined by the amount of heat lost through the roof, entry ways and walls.
Evaporator Coil—Part of a split-system air conditioner or heat pump located indoors. The evaporator coil cools and dehumidifies the air by converting liquid refrigerant into a gas, which absorbs the heat from the air. The warmed refrigerant is then carried through a tube to the outdoor unit (condenser coil).
Fan Coil—An indoor component of a heat pump system, used in place of a furnace, to provide additional heating on cold days when the heat pump does not provide adequate heating.
HVAC—Term used for Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning
HSPF—The Heating Seasonal Performance Factor is a measure of the heating efficiency of a heat pump. The higher the HSPF number, the more efficiently the heat pump heats your home.
Horizontal Flow—A type of furnace, installed on its "side," that draws in air from one side, heats it and sends the warm air out the other side. Most often used for installations in attics or crawl spaces.
Humidifier—Machine that adds water vapor to heated air as it moves out of the furnace. This adds necessary moisture to protect your furnishings and reduce static electricity.
Matched System—A heating and cooling system comprised of products that have been certified to perform at promised comfort and efficiency levels when used together especially when implemented according to design and engineering specifications.
Operating Cost—The day-to-day cost of running your home comfort equipment, based on energy use.
Payback Analysis—Overall measure of the efficiency and value of your home comfort system. By combining your purchase price and ongoing operating costs, a payback analysis determines the number of years required before monthly energy savings offset the purchase price.
Perfect Heat™—The Perfect Heat gas furnaces use a two-stage valve and patented control algorithm allowing the furnace to more closely meet the heating needs of the home. A Perfect Heat heat pump controls the airflow across the indoor coil and controls auxiliary heater banks to deliver warmer, more comfortable air to the home.
Perfect Humidity™—Perfect Humidity will remove excess moisture from indoor air to help eliminate that warm, sticky, uncomfortable feeling you get in high humidity. Add a humidifier and the system provides Perfect Humidity in heating.
Puron™ Refrigerant—Puron is an environmentally sound refrigerant designed to protect the earth's ozone layer. Federal law requires all manufacturers phase out ozone depleting refrigerants in the next few years. Puron is approved by the US Environmental Protection Agency as a replacement from Freon 22*.
SEER—The Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio is a measure of the cooling efficiency of your air conditioner or heat pump. The higher the SEER number, the more efficient the system is at converting electricity into cooling power.
Setback Thermostat—A state-of-the-art electronic thermostat with a built-in memory that can be programmed for different temperature settings at different times of the day.
Split System—Refers to an air conditioner or heat pump that has components in two locations. Usually, one part of the system is located inside (evaporator coil) and the other is located outside your home (condenser coil).
Upflow—A type of furnace that draws cool air from the bottom and blows the warmed air out the top into the duct work.
Ventilator—A ventilator captures heating or cooling energy from stale indoor air and transfers it to fresh incoming air.
Zone Perfect™—Our exclusive zoning system, designed to work in conjunction with properly matched HVAC products to enhance energy efficiency by as much as 30%.
Zoning—A way to increase your home comfort and energy efficiency by controlling when and where heating and cooling occurs in a home. Programmable thermostats are used to control operating times of the equipment. Dampers are used to direct air flow to certain parts or "zones" of the home.
* Freon is a trademark of E.I. Dupont.